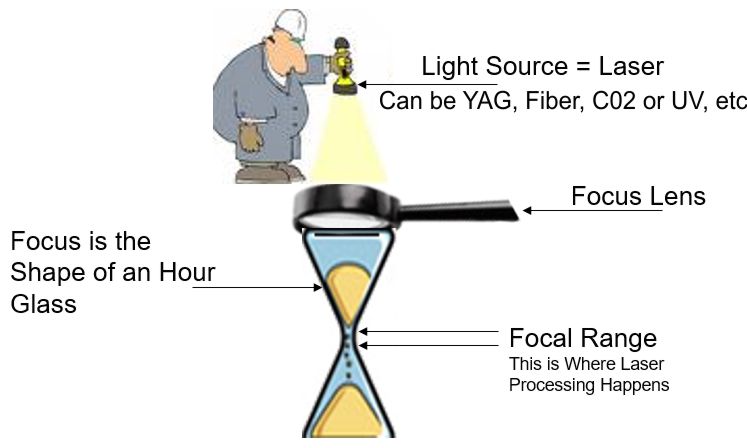
What Happens is Really Quite Simple
- A laser is simply a source of light. In this case, we use a flashlight as an analogy
- The light can be one of many different wavelengths – Fiber, C02, Green, UV, etc
- Material determines which laser is best as laser energy will “absorb into” or “bounce off”
- Laser light can be delivered many ways such as flatbed, galvanometer (galvo) or fixed head
The laser beam is delivered primarily using 3 methods
Galvanometer
- Marking
- Annealing Steel
- Deep Engraving Metal (fiber)
- Thin Material Cutting
Flatbed (XY Plotter)
- Marking
- Annealing (fiber)
- Engraving
- Cutting up to 1″
Fixed Head
- Cutting
- Welding
VERY General Overview of Differences
Galvanometer
- Speed
- Vectoring (hotter beam)
- Typically greater focus range
Flatbed (XY Plotter)
- Batch process (start and forget)
- Open Architecture (use any design software
- Larger, continuous process area
- Better for cutting compared to galvo
Fixed Head
- Parts translate using XY table
- Clean thin metal cutting
- Gas jet nozzle
- No alignment issues